The research team led by Professor Guodong Chen from the First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China has published a cutting-edge paper titled “Conversion Therapy Strategy: A Novel GPC3-Targeted Multimodal Organic Phototheranostics Platform for Mid-late-stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma” in the prestigious international journal Materials Today Bio (Chinese Academy of Sciences Quartile I, Medicine; Impact Factor: 8.7). In this study, the team developed a near-infrared (NIR) phototheranostic probe and investigated its application in conversion therapy for mid-late-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), demonstrating significant suppression of tumor recurrenceimprovement in patient prognosis.

HCC is the most common primary malignancy of the liver. It often develops insidiously,is typically diagnosed at intermediate to advanced stage, making surgical resection unfeasible. Conversion therapy aims to convert initially unresectable tumorsresectable ones, thereby enabling surgical intervention and maximizing patient survival. However, the effectiveness of traditional conversion therapies remains uncertain, highlighting the urgent need for innovative approaches. Near-infrared phototheranostics technology provides a new way for HCC diagnosistreatment by its excellent optical properties. However, complex preparationpoor biocompatibility of phototheranostics probes limit clinical application.
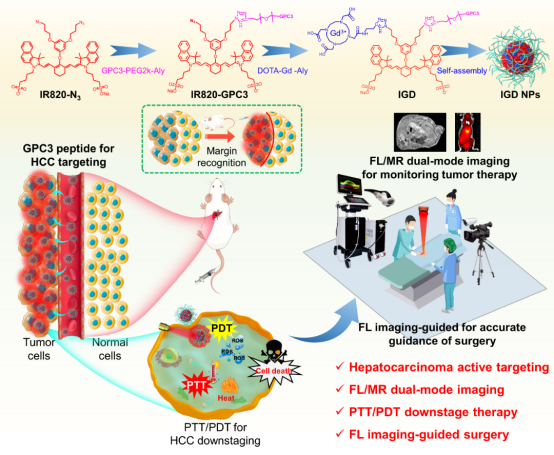
In this study, the joint team of Professor Guodong ChenDr. Qinglai Yang developed a GPC3-targeted multifunctional phototheranostic probe named IGD NPs, integrating fluorescence/magnetic resonance dual-modality imaging (FLI/MRI) with photothermal/photodynamic therapy (PTT/PDT), to improve the efficiency of conversion therapy for HCC. The IGD NPs were simply prepared with the IR820 as the core. Using click chemistry, the HCC-specific targeting molecule GPC3 peptidethe MRI contrast agent DOTA-Gd are conjugated to form the probe. IGD NPs target HCC cells via GPC3 and, under noninvasive 808 nm laser irradiation, release heatreactive oxygen species (ROS) to reduce tumor sizeachieve downstaging. High-sensitivity FLI/MRI precisely delineates tumor boundaries, providing real-time surgical navigation,prognostic assessment. This novel probe offers a feasibleeffective treatment option for advanced HCC.
The first authors of the paper are Fan WuXin Kuang, both master’s students specializing in hepatobiliary surgery. The co-corresponding authors are Professor Xiaofeng Tan, Dr. Guilong Wu,Professor Qinglai Yang from University of South China, as well as Professor Guodong Chen from the First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China.
For years, the joint team led by Guodong ChenQinglai Yang has been dedicated to research on NIR-II organic molecular theranosticsimmunotherapy for hepatopancreatobiliary tumors, achieving a series of groundbreaking results. Their work has been published in high-impact journals such as Advanced Science, Theranostics, Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, Analytical Chemistry,Materials Today Bio. This study was funded by the National Science Foundation of China, the Key ResearchDevelopment Program of Hunan Province, China, the Central Government Guided Local ScienceTechnology Development Fund Project in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region,the University of South China Clinical Research 4310 Program.
Link to original article:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101442